This post is to show how to evade anti-virus detection using the Veil framework, which is a set of tools built for penetration testing.

A Complete Guideline towards the first step that will create a barrier between you and cyber attacker.
The Internet enables businesses of all sizes and any location to reach new and larger markets, provides the opportunity to work more efficiently with the help of computerized tools. Whether a firm wishes to implement cloud computing or just use email and maintain a web site, cybersecurity must be part of the plan. Stealing digital information has become extensively reported fraud, beating physical theft. Every business using the internet has a responsibility to create a safety culture that builds business and consumer confidence.
As a small business holder, several questions may arise in the mind like Why is cybersecurity important for small businesses? What harm could an attacker do when you don’t have billions in your account but a data breach can happen anywhere regardless of the size of the business. Implementing a small checklist for cybersecurity is the first step to secure your digital assets. You might think that your business is not big enough to be aimed for this kind of attack. But it’s quite the reverse small companies rarely provide capital for security measures and training, so they end up being the prey for such invaders.
Empowering and Securing the SMEs With Technology
Due to this epidemic of Covid-19 CEOs of all businesses face overwhelming tasks and unmapped waters of the fast-digital transformation of their services. The cyber attacker are actively searching for such firms with vulnerabilities to attack.
According to a recent independent agency survey, 88% of SME house owners in their business felt vulnerable to a cyber attack.
Consider these statistics:
As reportable by the 2019 Verizon knowledge Breach Investigations Report, 43% of cyber-attack victims are little businesses.
Within the last 12 months, nearly (47%) of SMBs have suffered cyber-attacks.
The price of a cyberattack on a business is $200,000, which is discouraging, particularly for little corporations with no cybersecurity plans.
Recent research shows that almost 60% of SMBs fold after 6 months of a cyber attack.
In less than a year, Indian companies have seen several ransomware attacks – WannaCry, GoldenEye, and the latest, Locky. Ransomware is a malware that hijacks computers, encrypts important files, denies access to the2m, and then asks the victim to pay ransom to have the files decrypted.
Although very few companies report cyber attacks due to the fear of reputation loss, experts believe Indian companies have been hit hard by ransomware because they are ill-prepared for cyber threats. India was The Third Strongest Country of WannaCry, according to a Kaspersky Labs report. The number of users attacked by ransomware in India has almost doubled from 2015-16 to 2016-17.
A 2016 survey by cybersecurity firm ESET in the Asia-Pacific region found that Indian SMEs have been most vulnerable to cyber attacks in the past three years. The lack of qualified hands that SMEs can manage, sign-on, insufficient cybersecurity assets, business deals on smartphones, and negligent staff are some of the main reasons for SMEs to be a threat. However, the biggest trouble for Indian SMEs is emerging technology. Rapidly transforming cybersecurity technology leaves SMEs uncertain of the solutions that best suit them.
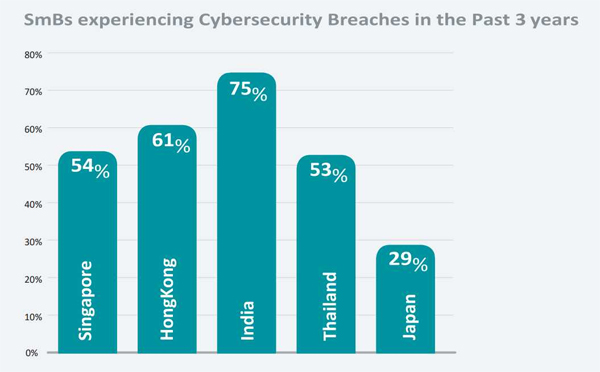
6 Key Challenges faced by SMEs
The BYOD problem: Bring-Your-Own-Device (BYOD) is usual now that staff assumes that it’s safe to use their gadgets to access corporate data. This is crucial trouble for SMEs. While companies can keep their own devices protected, they have no authority over private gadgets. Elevating awareness in the staff members is the only key to this issue.
Outsourcing: To remain alert and sharp, SMEs work together with several third-party vendors. These vendors may have sensitive information about them, but they may not have the cybersecurity measures in place to prevent an attack. 19% of SMEs acknowledge this risk as a challenge. Small businesses need to consider options like authentication and network monitoring.
Absence of arrangement: As SMBs grow, cybersecurity may not remain a top priority as more demanding needs emerge as the business grows. This challenge becomes even greater when the same cybersecurity team is tasked with other growth projects that are seen as more important. 24% of SMEs see this as an obstacle.
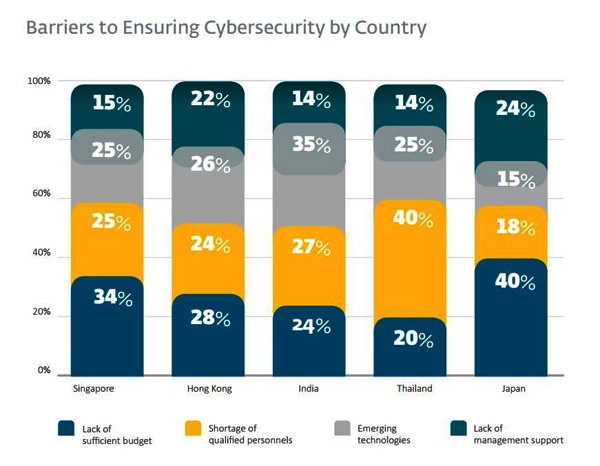
Budget woes: The ESET survey found that capital remains the biggest hurdle to cybersecurity for almost a third of companies. Smaller SMEs (35%) find it explicitly difficult to justify the funding required, especially when such funds can be used for other purposes. In developed countries like Japan (40%), Singapore (34%), and Hong Kong (28%) the lack of adequate budget is evident compared to emerging countries like India (24%) and Thailand (20%).
Staff shortage: The lack of qualified personnel is also high on the list of obstacles in embracing cybersecurity. 27% of companies consider there is a lack of experienced professionals to hire. This is not surprising when you consider that cybersecurity has only played an important role in the past few years. The demand for cybersecurity professionals is currently outrun those available.
Evolving technology: Another obstacle with the adoption of cybersecurity is that the persistently altering technological environment. SMEs are unsure where and when they ought to invest in a solution as they’re afraid that they are not investing in the latest technology. They are concerned about how well the technology suits their organization.
These were the key points that brand SMEs vulnerable, However, Let’s talk about the points that may assist you to shield your organization from cyber attack.
14 Cybersecurity Tips to the SMEs
Expect a crisis: Unfortunately, an encounter with a security threat is an event of “when” not “if.”
Acknowledging a crisis is undemanding when a system-wide response plan is already in place.
Perform a risk assessment: Assessment of the IT security risk helps to make a property disaster recovery strategy and protects your vital assets from threats.
A risk assessment can reveal the following:
Your most beneficial assets: servers, websites, client data, trade secrets, partner documents, client data (credit card details, etc.)
The most crucial threats to your business: natural disasters, system failures, accidental human interference, and malicious human actions.
Vulnerabilities that a threat will use to compromise your security: previous instrumentation, untrained workers, unpatched or out-of-date package.
How to enhance your security status: Take satisfactory preventive and mitigation measures.
Protect client associated proprietary Data: If your company shares information with third parties via an external portal, there's a risk of a felony.
Recognize all third parties and their vulnerabilities.
Illuminate shared information and avoid leaky spare data.
Put controls in place between your company and also the third-party company to exclude these approaches from the remainder of the business.
Detect intrusions through mobile devices: You and your employees are likely accessing corporate data on mobile devices. These devices are often the easiest entry point into corporate databases.
Identify all the devices that connect with the company and those who have access to them.
Clarify security elements in the device: passwords, encryption, or others.
Make sure these devices can be wiped remotely so your company can keep control of their content.
Explain the authority of device users to access corporate data.
Evaluate BYOD policies: Have you identified data breaches from employee-owned devices? A BYOD strategy carries risks and opportunities that you should evaluate regularly.
Confirm the number of devices connecting to your network.
Review your enterprise-level security solution for employee mobile devices to maintain cost-effectiveness.
Maintain a strong password policy: Set strict criteria for employee passwords to prevent unwanted access.
Implement multi-factor verification for additional account protection.
Password changes are required on a schedule or in the event of a data breach.
Prohibit employees from sharing credentials.
Encourage the use of password generators to ensure password complexity.
Provide encrypted password managers to store passwords securely.
Encourage employees to use different passwords for each of their accounts.
Employ best practices on payment cards: Work with banks or processors to confirm the most trusted and valid tools and anti-fraud services are being used.
You may additionally have security obligations consistent with agreements along with your bank or processor.
Separate payment systems from substitutes, less secure programs, and don't use the same computer for expenditures and surf the Internet.
Use multiple layers of protection: Consider taking a layered approach, also known as Layered Security or Defense in Depth (DiD). With layered security, deliberate redundancies are established so that in the event of system failure, another system is immediately activated to prevent an attack.
Maintain current web browsers, operating systems, and security patches.
Set up antivirus software and run scans for software updates.
Deploy firewalls and intrusion protection systems in your network.
Use a virtual private network (VPN) to secure corporate Internet traffic.
Analyze data integrity to identify suspicious behavior.
Use behavior analysis to send alerts and run automatic controls when other methods fail.
Limit user access: Each access point carries an individual risk. Restrict user access to certain data that they need to perform their tasks.
Prohibit software installation without administrator rights.
Enforce email limitations: Email could be a common entry point for cyber criminals and malware. It is common to scam staff with phishing scams and malicious links in email messages.
Use message encryption, spam filters, and anti-virus software to prevent threats from achieving their intended goals.
Conduct employee awareness training to educate users on common fraud incidents and prevention techniques.
Secure your Wi-Fi: An unsecured WLAN can open your network to anyone, including hackers.
Flip your Wi-Fi passwords to protect your network.
Use separate guest and corporate networks.
Limit the session of the guest network.
Backup your data: The loss of vital corporate data or resources through hacking or emergencies will place a small business out of business.
Schedule backups frequently.
Store backup data in the cloud or other external storage.
Evaluate and test the whole data recovery procedure. Once successful, hackers constantly return the same routes to hack again.
Train employees on security protocols: When you've trained your employees on your safety guidelines, hold them accountable to follow them.
Compliance with security standards required.
Test your team's knowledge after a training session.
Employee signatures are required when implementing new policies.
Update policies regularly: Make sure your security policy and cybersecurity training curriculum are relevant and updated regularly.
Stay up to date on the latest IT security trends.
IT staff must earn cybersecurity certifications.
Conduct cybersecurity training regularly.
Conclusion
Having a dedicated IT department is becoming crucial for every business. Your IT department needs to be able to quickly find and control problems. There will be violations. This checklist can reduce the probability but no security defense is resistant. You must have a system and strategy to find and control problems across the network. Network security is no longer elective. It’s a prerequisite for every business, no matter the size of the business.
Users also read:
How to perform Man in the middle attack with Ettercap
Man in the middle attack allows the attacker to eavesdrop between clients, servers, and people. This attack may include HTTPS connections, SSL/TLS connections, and more. In this tutorial, I am going to use Ettercap to perform Arp poising in the man-in-the-middle attack with the help of Wireshark.
How To Access Android Phone Camera Using Kali Linux
In this tutorial, we will take a picture from the victim's smartphone camera without their knowledge. However, please note that this is post is for educational purposes and I have no responsibility for any illegal activity.

