This post is to show how to evade anti-virus detection using the Veil framework, which is a set of tools built for penetration testing.

In this era of technology, the internet has become a key element of people's life especially in this pandemic of COVID-19. It has given a real meaning to the world “global village” with the economy’s interconnected with digital technology. India is the second-largest internet population with over 700 million users. While this provides great connectivity to the world but it also leaves us open to new vulnerabilities.
People started relying more on technology due to various reasons. However, as it’s said everything has two sides as a coin technology also has two sides. The first one is that it provides effortlessness in both professional and private life but on the other side the side it is easy to use technology to create scams and fraud.
An E-mail has become an integral part of professional life, but as soon as it started to be used widely it has become one of the easiest ways to fraud or scam people. E-mail fraud is the intent to deceive an individual by way of email for personal gain or harm, it can easily take the form of a “con game” or “scam”.
Let’s take a look at the common type of E-mail frauds.
7 Common Types of E-Mail Frauds
1. Executive Scam
Executive Scam is the scam whose purpose is to jeopardize the structure of the corporation. They are fraud in which cyber criminals access high-ranking managers' email accounts through techniques like spear-phishing. Unauthorized operators may become legal owners and order other workers to perform a range of operations, such as the transfer of large amounts of money to foreign accounts. Because of its high success rates, Executive fraud is common. Executive fraud offers the best chances for attacks without detection. Executives generally teach their subjects by email.
2. Online Banking Scams
The internet allowed organizations like banks to give customers services over the internet. This culminated in the frequent use of phishing attacks by email to increase online banking scams. An unsuspected victim receives an e-mail indicating that his bank has some issues that can be addressed by logging into his online account. However, the user is redirected to another website similar to the official online banking platform by clicking on the given URL that may provide the correct URL address. The scammers can acquire any credentials on the dummy website and use them to transfer to the account of the victim.
3. Survey Scams
Survey scams include emailing a victim of an online survey for statistics or winning a draw. An Internet con artist studies the needs of the aim for the first time. This is also achieved via Social Engineering. The victim's email message may contain information that appeals to their interests and strong reasons for participating in the surveys. When you click the survey link, malicious scripts will install on the computers of the victim automatically. Among other items, cyber criminals can access highly confidential information such as usernames, passwords, or vital accounts remotely from a computer. The effect is the use of information maliciously or by cyber criminals to commit cyber crime of all kinds.
4. Employment Scams
The value of fraudulent email to frauds and scams is depending on online con artists. As such, they are commonly used to encourage victims to share personal information such as legal identities, social security numbers, and bank details. The fraudulent emails can seem from a reputable business to drown suspicions. Upon receiving the e-mail, the victims are asked to provide the details "so that they can start working immediately." the sudden job opportunity. However, the scammers will use it with their hands on this precious information to steal the identity of the victim, clear their account banks, or use it in fake money orders for various services.
5. Refund & Reward Scams
Internet scammers can be dangerous to e-mail fraud attacks by the victims. They may apply various techniques to their plans for work, including monetary incentives. For example, an email may state that the sender has a rich relative who can not have access to his money and who needs financial assistance for some reason. The scammer could request financial assistance with the bank details of the victims for "refund and incentive" purposes. In other situations, they may be saying that they want a bank account, offering a good incentive for exchanging money or goods in another country. Nevertheless, the scanners use the details given to access and vacate the bank accounts of victims. These forms of e-mail frauds are widespread because the vast majority of the victims are compensated.
6. Sale Scam
The desire for individuals to purchase new goods that are not yet released to the consumer market can be exploited by cyber criminals. This ensures that new items such as smartphones or video games can be sent with e-commerce e-mails at low prices Given the low prices and the lack of product launches, some people will pay for the sales. Some people will not. Of course, the items bought will never be shipped, and the victims will wait for days. Such forms of email fraud can also be intended to gain personal information on the victim, for example, credit card numbers. To buy their own illegally items cybercriminals can use the details.
7. Bill Scam
There are often online shoppers' email frauds. Victors can receive e-mails saying they can not deliver the product they have ordered because of billing address errors. The e-mails contain links to spoofed sites where attackers can access information from the credit card when they fall into the pit. Various methods can be used by attackers to improve their success rates.
Well, Above were some common e-mail frauds. Now let’s take a look at the 7 most common trends that attackers use to do e-mail fraud.

7 Most common Trends of E-mail Fraud
1. Error In Grammar & Spelling
Bad spelling and the wrong use of grammar is one of the most common indicators of a phishing text. Many organizations have the spell control function turned on for outbound emails by their email customers. Automated or highlighted functionality can also be implemented on most web browsers. Thus you would assume the grammar and orthography free e-mails coming from a reliable source.
2. Threats or desperate requirement
E-mails threatening harmful results should be always viewed with concern. Another strategy is to use a sense of urgency to inspire or even to request urgent action in an attempt to flush the recipient. The scammer hopes that the material can not be checked extensively when the e-mail is read quickly so that other anomalies related to a phishing campaign are not identified.
3. The Susceptible stats
Where an email is sent from an unknown source with an attached file or where the recipient has not requested or is expecting an email sender to file it should open the attachment with caution. When the attached file is typically associated with malware downloads (.zip,.exe,.scr, etc.) or has an unfamiliar extension, the file should be flagged by the beneficiaries that are checked until opening.
4. Extraordinary request
If the email asks for something that is not the norm to be done, then that, too, is an indication that the message could be malicious. For instance, if an email appears to be from the IT team asking for software to be installed, or a link followed to patch the PC, but this type of operation is normally done centrally, that's a major indicator that you've received a phishing email and you should not follow the instructions.
5. Small and lovely
While many phishing e-mails are full of details designed to offer false security, there is also little information about phishing messages that hope to deal with the ambiguity of them. For example, a scammer, who spoofs an electronic mail from Jane to a business that is a favorite vendor emailing the firm once or twice weekly, is given the ambiguous message 'here's what you requested.
6. Credentials query, payment information, or other personal information
One of the most advanced forms of phishing emails is when an intruder created a phony landing page, where recipients are addressed by an official email address. The phony landing page has a login box or needs payment to fix a remaining problem. If the e-mail is unexpected, recipients can visit the place where they allegedly have e-mail by typing in the URL – instead of clicking on a link – to prevent entering their login credentials or paying the intruder.
7. What you do not see is what you get
In a phishing attack, you don’t get what you see. For example, In a hoax e-mail, it may say that it’s regarding the sale on an e-commerce site you usually shop from but in the attachment, you will find a zip file that contains malware.
Alright until now we have covered topics that include common frauds done by email and common trends that are mostly easy to recognize if they are looked at with significance. Now, Let’s move on to the checklist that will help you keep safe from falling for e-mail scams. Let’s dive in!
Below are the 10 email scam safety precaution checklist that will help you keep safe.
10 E-Mail Scam Safety Precautions
Cybercrime commonly occurs via e-mail (e.g spam, phishing, and online scams). As well as being alert to suspicious or unsolicited messages you should consider the following useful checklist to avoid falling victim to cybercrime.
1.
Use spam filters on your e-mail account.
2.
Be suspicious of unsolicited messages, even from a person or organization that you know.
3.
Avoid opening suspicious or unsolicited messages with attachments & links to other Websites.
4.
Avoid replying & Forwarding suspicious messages.
5.
Never hand out your personal information to suspicious emails from unknown sources.
6.
Seek expert advice before sending money to an unknown person or organization.
7.
Read terms & Conditions Carefully.
8.
Check your bank statements regularly to keep an eye for any suspicious transaction.
9.
Shred unwanted documents that contain your sensitive information.
10.
Remember if it’s too good to be true then it probably is!
Examples of Email Fraud
In this example, we are going to look at the example of an employment Scam. In the given image below. It seems as the company has gone through your resume and is offering you a job along with benefits that you’ll receive while working from home.
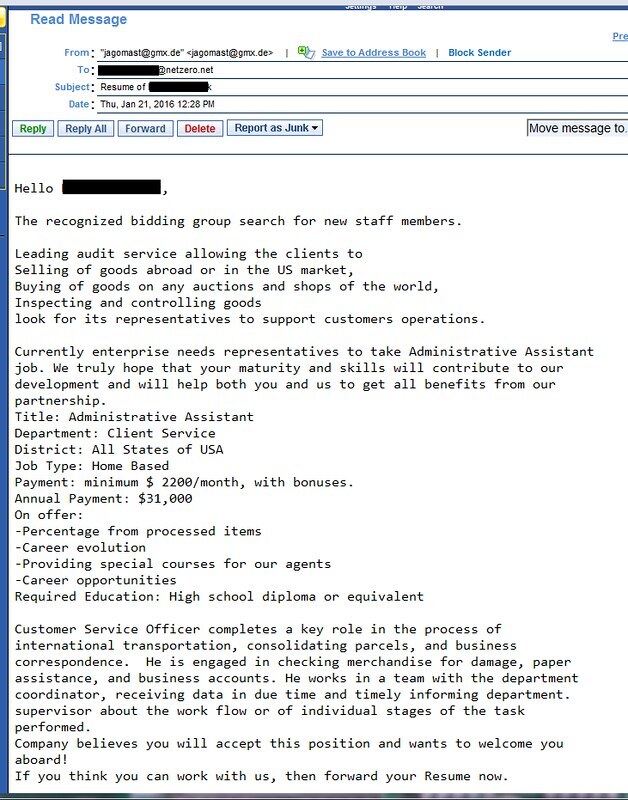
Look closely at the email how can know that this is a phishing email? How can you know that this scam? Let’s see some points that you can notice in the email that makes it suspectable email.
GMX is an email service free of charge, but it's not a business address ... What's more, the German server is describing the uncomfortable Google Translate rendition of the body of the text.
There's something fishy if you can't name the company for which you're promoting or can't include an internal email address.
"The company thinks you're going to take this role" ... Company overestimates the gullibility of individuals.
Also, if they have read the title "resume of (your name)" and that's why they're contacting you, but the last line is "give us your resume" as they haven't ...
Let’s take a look at another example this time Tech Support.
Online service providers have stepped up their safety game over the past few years by contacting consumers when they find suspicious or alarming behavior on the profiles of their users. Not surprisingly, this is being exploited to their benefit by the bad guys. Many are poorly designed with bad grammar, etc., but others seem legitimate enough for anyone to click if they do not pay close attention:
Find this bogus PayPal security alert warning on their accounts of possible "unusual log in operation" marks:
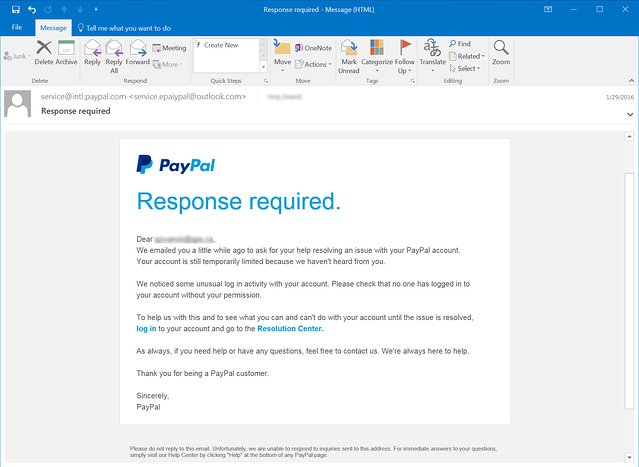
If you read this type of email carefully and hover over the links it will be enough to save you from ending up stealing website credentials.
Conclusion
Phishers are developing and striking at new speeds. Although the end goal of phishing is still the same, the top goals of spoofing shift and e-mail filter bypassing methods are more advanced than ever. For keeping business safe it’s important to train employees to not directly click on any link that is sent to them. Being a little careful while reading your emails can save you from being the victim of email fraud.
Users also read:
How to perform Man in the middle attack with Ettercap
Man in the middle attack allows the attacker to eavesdrop between clients, servers, and people. This attack may include HTTPS connections, SSL/TLS connections, and more. In this tutorial, I am going to use Ettercap to perform Arp poising in the man-in-the-middle attack with the help of Wireshark.
How To Access Android Phone Camera Using Kali Linux
In this tutorial, we will take a picture from the victim's smartphone camera without their knowledge. However, please note that this is post is for educational purposes and I have no responsibility for any illegal activity.

